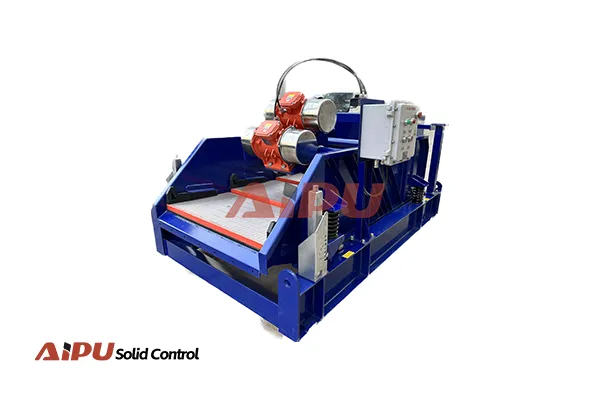
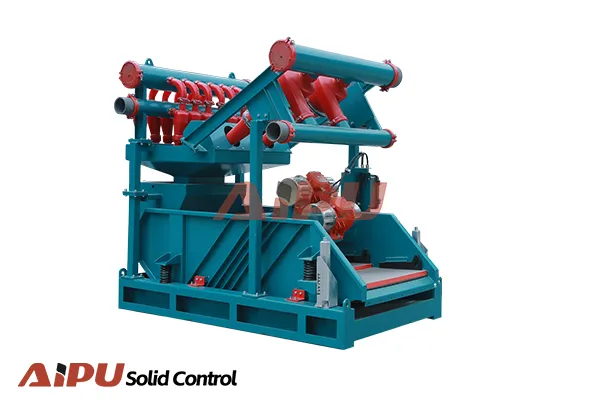
Mud Cleaner for Water-Based Drilling Fluids: Configuration, Role, and Optimization
The mud cleaner is a highly adaptable and critical component in water-based drilling fluid (WBM) systems. Its configuration and operational focus differ notably from its use in oil-based systems, primarily due to the lower fluid cost, higher solids tolerance thresholds, and different environmental considerations.

Core Challenges in Water-Based Drilling Fluids
-
Abrasion & Rheology: Fine drilled solids (silt) are the primary enemy, causing abrasive wear and increasing plastic viscosity and gel strengths, which reduces drilling efficiency.
-
Fluid Cost vs. Disposal Cost: While WBM is less expensive per barrel than OBM, high-volume onshore disposal costs and offshore discharge regulations (governed by particle count and toxicity) make efficient solids removal vital.
-
No Intrinsic "Value" in Fines: Unlike weighted OBM, there is no high-value liquid to recover from the solids. The goal is maximum removal of undesirable fines.
Primary Role in WBM Systems
In WBM, the mud cleaner acts primarily as a high-efficiency, fine-solids removal and drying device. Its purpose is to protect the fluid's properties and downstream equipment by removing abrasive particles in the 15-74 micron range that the shale shaker misses.
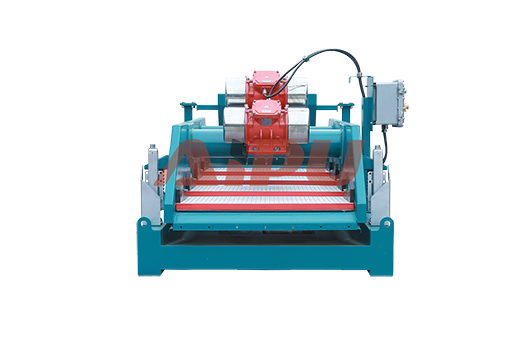
Typical Configurations for WBM
The mud cleaner is most effectively used in one of two configurations, depending on whether the mud is unweighted or weighted.
1. For UNWEIGHTED Water-Based Muds (No Barite)
-
Configuration: The mud cleaner is often configured as a combined desander/desilter unit.
-
Process Flow:
-
Fluid from the shaker tank is pumped to the mud cleaner's desander manifold (10" cones).
-
The desander overflow (solids-removed fluid) feeds directly into the desilter manifold (4" cones).
-
The underflow from both the desander and desilter is combined and discharged onto the unit's single, fine-mesh vibrating screen.
-
-
Result: This provides two-stage hydrocyclone separation (removing both sand and silt) with a final drying stage on one compact skid. It maximizes solids removal and returns clean fluid to the active system.
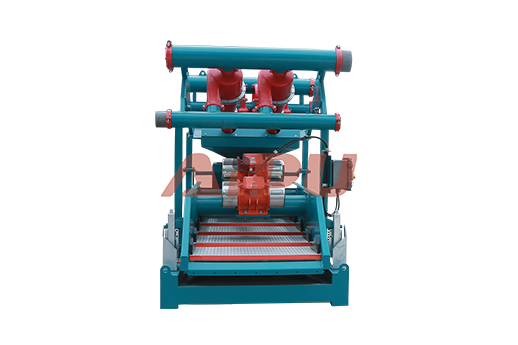
2. For WEIGHTED Water-Based Muds (With Barite)
-
Configuration: The mud cleaner is configured as a desander underflow processor and barite recovery unit.
-
Process Flow:
-
A desander (a separate unit) processes the shaker effluent. Its overflow (with barite and fines) goes to the mud cleaner feed tank.
-
The desander's underflow (concentrated sand and some barite) is routed to the mud cleaner.
-
The mud cleaner's hydrocyclones (4" cones) further concentrate the slurry, which is then screened.
-
The fine screen (150-200 mesh) allows barite to pass through while retaining the lower-specific-gravity drilled solids.
-
-
Critical Note: The desilter function is typically BYPASSED in weighted WBM. Running a desilter would discard valuable barite with the silt, as it cannot differentiate between them. The mud cleaner's screen provides the selective recovery.
Key Operational Adjustments for WBM
-
Screen Selection: Screens are generally coarser than in OBM systems, typically in the 150 to 200 mesh range. The focus is on throughput and preventing screen blinding from sticky clays. Drying efficiency is still important to reduce waste volume.
-
Hydrocyclone Apex: Adjusted to achieve a "spray" discharge, optimizing the balance between solids separation and minimizing fluid loss to the screen.
-
Flocculants & Dilution: In WBM, chemical flocculants are often added upstream of the mud cleaner to "grow" fine particles, making them easier for the hydrocyclones to remove. Strategic dilution may also be used to control feed density.
Advantages in a WBM System
-
Superior Solids Control: Provides the most effective and economical removal of abrasive silt-sized solids, protecting pumps and drill strings.
-
Maintains Optimal Drilling Hydraulics: By controlling fine solids content, it helps maintain low viscosity, improving rate of penetration and hole cleaning.
-
Enables Weighted Mud Efficiency: Makes the use of barite practical and economical by preventing its wasteful loss during necessary desanding.
-
Reduces Waste and Environmental Impact: Produces a drier, more solid waste stream, which lowers disposal costs and minimizes the liquid footprint of reserve pits or offshore discharge volumes.
-
Cost-Effective Simplicity: The combined desander/desilter/screener design for unweighted muds offers excellent performance in a single, low-maintenance package.
Comparison: Mud Cleaner in WBM vs. OBM Systems
| Feature | Water-Based Mud (WBM) | Oil-Based Mud (OBM) |
|---|---|---|
| Primary Goal | Maximize fine solids removal; Recover barite. | Maximize base oil recovery; Dry cuttings. |
| Screen Mesh | Coarser (150-200). Focus on flow. | Finer (200-250+). Focus on drying. |
| Key Value Driver | Protecting equipment & drilling efficiency. | Recovering high-cost fluid & waste reduction. |
| Desilter Stage | Used aggressively in unweighted muds; Bypassed in weighted muds. | Often minimized or bypassed to avoid fluid loss. |
| Waste Concern | Volume and chemical toxicity of aqueous phase. | Retained Oil on Cuttings (OOC) and hydrocarbon volume. |
Conclusion:
In water-based drilling fluid systems, the mud cleaner is a versatile workhorse for fine-solids management. Its configuration flexes to meet the specific needs of unweighted and weighted muds, but its core mission remains: to remove the abrasive, viscosity-building fines that hinder performance. For unweighted muds, it acts as an efficient, all-in-one desander, desilter, and dryer. For weighted muds, it becomes the guardian of barite, ensuring it is not wasted during essential desanding operations. By extending fluid life, protecting expensive equipment, and reducing waste, the mud cleaner delivers a compelling return on investment and is a fundamental component of a modern, efficient WBM solids control system.