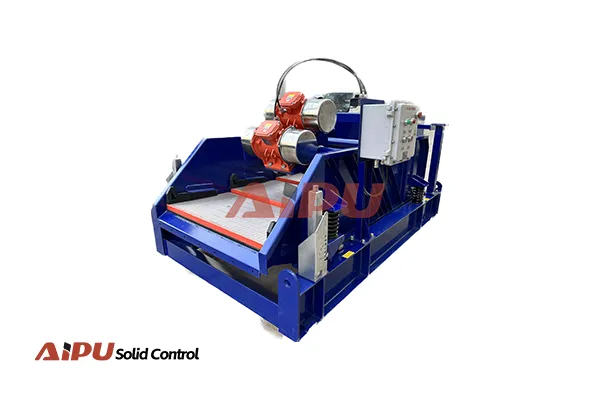
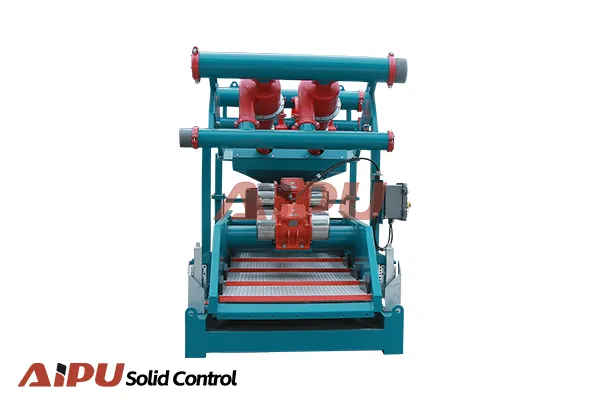
mud cleaner in drilling mud recycling system
Within a closed-loop drilling mud recycling system, the mud cleaner serves as a pivotal recovery and purification node that transforms waste streams into reusable resources. Its positioning and function are essential for economic efficiency and environmental sustainability in modern drilling operations.

The Recycling System Context
A drilling mud recycling system is designed to maximize the reuse of drilling fluid by continuously removing drilled solids while preserving the liquid and chemical components. The system follows a cascading separation process where the mud cleaner occupies a strategic middle position.
Typical Recycling Loop:
-
Primary Separation: Shale Shakers → Removes coarse cuttings (>75µm).
-
Secondary Recovery: Mud Cleaner → Processes shaker effluent; recovers fluids & valuable solids; discharges fine waste.
-
Tertiary Polishing: Centrifuges → Removes ultra-fines; further recovers weight material.
-
Chemical Reconditioning: Treated fluid returns to mixing/active tanks for property adjustment and reuse.
The Mud Cleaner's Specific Recycling Functions
1. Value Recovery from Waste Streams
-
Recovers Weight Material: In weighted muds, the mud cleaner salvages 90-95% of barite from the desander underflow that would otherwise be lost. This is the single most important recycling function, as barite represents a major ongoing cost.
-
Recovers Liquid Phase: Recovers both base fluid (oil or water) and expensive chemical additives (polymers, emulsifiers, etc.) from what would become waste, directly reducing the need for fresh fluid makeup.
-
Concentrates Waste: By producing a drier solids discharge, it minimizes the total volume of hazardous waste requiring disposal or further treatment.
2. Enabling Closed-Loop Economics
The recycling system's economic viability depends on the mud cleaner's performance:
-
Reduces Fresh Mud Requirements: Effective recovery cuts new mud purchases by 15-40% in typical operations.
-
Lowers Disposal Costs: Drier cuttings reduce waste hauling and processing expenses. Offshore, this can mean significantly lower skip-and-ship or cuttings processing costs.
-
Decreases Chemical Consumption: Recovered mud retains active chemicals, reducing the need for continuous re-treatment.
Integration in the Recycling Flow Path
For Weighted Mud Recycling:
Shale Shaker (Coarse Waste)
↓
Desander
↓ (Underflow: Sand + Barite + Liquid)
MUD CLEANER ←← Critical Recovery Point
↓
(Recovered: Barite & Liquid) → Returns to Active System
↓
(Discard: Dry Fine Solids) → To Waste Management
↓
Centrifuge → Polishing & Additional Barite Recovery
For Unweighted Mud Recycling:
Shale Shaker
↓
MUD CLEANER (as combined desander/desilter)
↓
(Recovered: Clean Liquid) → Returns to Active System
↓
(Discard: Dried Sand/Silt) → To Waste Management
Synergy with Other Recycling Equipment
-
With Shale Shakers: Accepts the shaker's liquid effluent, preventing it from becoming immediate waste.
-
With Centrifuges: Acts as a "pre-cleaner," removing the bulk of fine solids to prevent centrifuge overload. In weighted systems, the centrifuge then polishes the mud cleaner's recovered fluid for ultra-fine removal.
-
With Cuttings Dryers (for OBM): Often feeds its recovered fluid to a vertical cuttings dryer for final extraction, creating a two-stage recovery process that maximizes fluid return.
-
With Chemical Injection Systems: By maintaining stable solids content, the mud cleaner reduces the need for frequent chemical adjustments to control rheology.
Advanced Recycling: The "Zero Discharge" Objective
In environmentally sensitive areas, mud cleaners are crucial for approaching "zero discharge" operations:
-
Maximizes Fluid Reuse: Minimizes volume of fluid that eventually requires disposal.
-
Produces Handleable Waste: Dry cuttings can be further processed (e.g., thermal desorption for OBM) or safely contained.
-
Enables Bulk Cuttings Re-injection: Drier, more consistent cuttings are better suited for slurrification and re-injection into disposal wells.
Operational Optimization for Recycling Efficiency
-
Real-Time Monitoring: Tracking recovery rates (barrels of fluid recovered per hour) and discard dryness.
-
Feed Point Optimization: Drawing from the correct compartment (often the "sand trap") to ensure processing of the most solids-laden stream.
-
Screen Management: Using the finest mesh possible without sacrificing throughput to maximize liquid recovery.
-
Closed-Loop Testing: Regular mud checks downstream of the mud cleaner to verify it is maintaining target solids content and properties.
Economic Impact Assessment
A properly functioning mud cleaner in a recycling system typically shows ROI through:
-
Direct Savings: Reduced barite and fluid purchases.
-
Indirect Savings: Lower waste disposal costs, reduced water consumption (for WBM), and decreased transportation costs.
-
Intangible Benefits: Reduced environmental liability, smaller site footprint, and improved regulatory compliance.
Conclusion:
In a drilling mud recycling system, the mud cleaner is far more than just another solids control device—it is the primary economic engine of recovery. By strategically positioned between primary separation and final polishing, it captures value from waste streams that would otherwise represent pure cost. Its ability to selectively separate useful components (barite and liquid) from harmful solids (drilled fines) makes closed-loop mud management technically feasible and economically viable. As drilling operations face increasing pressure to minimize environmental impact and maximize efficiency, the mud cleaner's role in the recycling hierarchy becomes ever more critical, transforming linear "use-and-dispose" models into sustainable, circular fluid management systems.